Today is World Brain Day.
If you have a solid background in healthcare like I do, you’ll greatly and deeply appreciate and admire the human brain.
It’s such a wonder and beauty to behold.
You love it more when you see what it can do and how it does what it does.
You’ll also be scared to your bones when you see it get hurt and how that affects every other organ in the human body.
This year’s theme is thoughtful: Brain Health and Disability: Leave No One Behind.
From a young age, I’ve always been fascinated by the human brain and the nervous system in general.
While in school, I approached studying topics and subjects about the brain and nervous system with utmost desire and interest.
I think more people need to know more about their brains, what it does, how it does what it does and how to take care of it.
The whole idea of healthcare is about looking for safe ways to care for every organ in the human body (in health and disease).
When we are encouraged to eat healthy, the primary reason is to have adequate nutrients to meet the energy and nutritional needs of all organs in the body, from the stomach, lungs, heart, and pancreas to the bones and blood.
People need to know how to take care of their brains. They need to know that the brain is a fragile organ that must be nurtured correctly for it to perform optimally.
World Brain Day serves as a global annual reminder of how important the brain is. And this year’s focus is on people living with brain disabilities and what we can do to take them along.
This article shares plenty of research, reports, health tips, expert opinion, and more about brain health and disability.
Let’s take a look briefly at the brain’s anatomy and physiology.
Brief Brain Anatomy And Physiology
The brain is like the supercomputer of our bodies, responsible for controlling everything we do, think, and feel.
It’s a complex organ with billions of special nerve cells called neurons, working together to create our thoughts, emotions, and actions. It’s protected by the skull, resting within its soft vault in a special fluid (cerebrospinal fluid).
The Central Nervous System comprises the brain and the Spinal Cord.
The spinal cord is a tube-like structure of highly specialised tissues protected by the backbone or vertebral column. It runs from the bottom of the brainstem (medulla oblongata) to almost the end of the spine (lower back).
The primary function of the spinal cord is to conduct impulses (nerve signals) from the brain to the body and from the body to the brain.
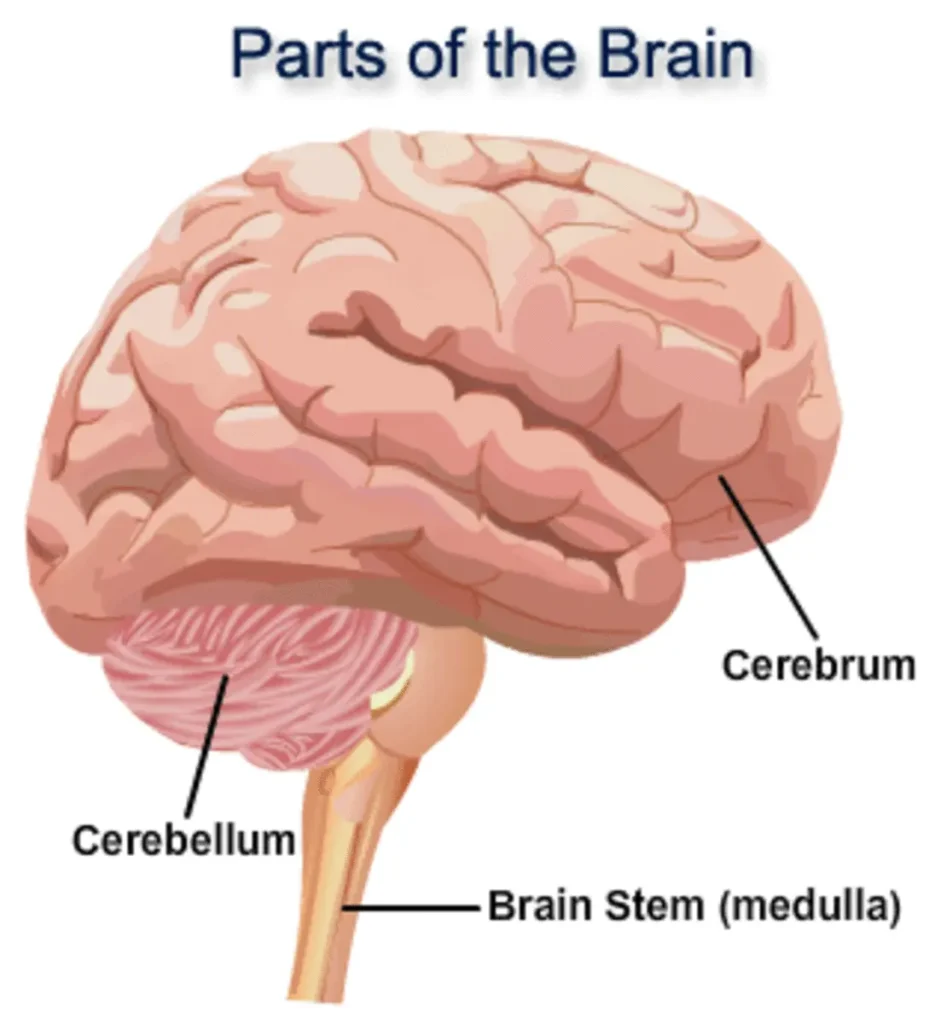
The brain can be divided into three main parts:
1. Cerebrum: This is the largest part of the brain, and it’s divided into two hemispheres. The cerebrum is responsible for conscious thoughts, emotions, language, and voluntary movements.
2. Cerebellum: The cerebellum (little brain), located at the back of the brain, plays a vital role in coordinating movement, balance, and posture. New studies are exploring the cerebellum’s roles in addiction, autism and schizophrenia.
3. Brainstem: The brainstem connects the cerebrum and cerebellum to the spinal cord and controls essential functions like breathing, heart rate, and digestion. The brainstem comprises the midbrain, the pons and the medulla.
Common Brain Disorders
Certain factors predispose people to develop brain disorders, from genetic factors and lifestyle to congenital disabilities and trauma.
Brain disorders can affect anyone, young or old, and significantly impact a person’s quality of life.
Here are some common brain disorders:
1. Alzheimer’s Disease: This progressive brain disorder negatively impacts memory, thinking, and behaviour. It primarily affects older adults and is the leading cause of dementia.
Parkinson’s Disease: The condition known as Parkinson’s disease was named in honour of James Parkinson, an English physician. Parkinson’s affects the nerves in the central area of the brain and is characterised by a gradual degeneration of these nerves due to the brain’s inability to produce enough dopamine, a neurotransmitter.
2. Stroke: When a blood clot or a ruptured blood vessel interrupts blood flow to a certain part of the brain, it leads to a stroke. The severity of brain tissue damage and impairments depends on the affected area. Strokes are common in both older and younger adults. According to experts, more younger people are having strokes because of obesity, high blood pressure and diabetes (about one in seven strokes occur in adolescents and young adults ages 15 to 49).
3. Epilepsy: Epilepsy is a neurological disorder characterised by recurrent unprovoked seizures caused by abnormal electrical activity in the brain.
4. Meningitis: Meningitis is a condition where the lining (meninges)surrounding the brain and spinal cord becomes inflamed. Infections, particularly bacterial and viral, are the typical causes of this disease. However, other factors such as fungi, drug allergies, and some cancers can also cause it.
Encephalitis: Where meningitis is the inflammation of the membranes surrounding the brain, Encephalitis is the inflammation of the brain.
5. Migraine: A severe headache disorder accompanied by visual disturbances and sensitivity to light and sound.
6. Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI): This occurs when the brain experiences a sudden, severe jolt or blow to the head, leading to various cognitive and motor impairments.
How To Take Care Of The Brain
The brain is one of the most delicate and enduring organs in the human body (how an organ can be so delicate and at the same time enduring is just amazing).
It has various natural means to protect itself from infection and trauma.
The Blood-brain barrier protects the brain from infections in the blood that would otherwise compromise the brain’s natural environment and cause serious harm to it if allowed to enter. While the thick skull and meninges (surrounded by cerebrospinal fluid) simultaneously function as biological cushions to prevent the brain from external trauma or force.
However, there are things we must also do to keep the brain healthy.
Here are some tips for maintaining a healthy brain:
1. Stay Mentally Active: Engaging in activities that challenge your brain, such as puzzles, reading, learning a new skill, or playing memory games, helps keep the brain sharp and improves cognitive function.
2. Eat A Brain-Healthy Diet: For optimal brain health, it’s important to maintain a balanced diet that includes plenty of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and healthy fats such as those found in fish and nuts. These foods provide essential nutrients that support brain function.
3. Exercise Regularly: Engaging in physical activity is beneficial for the body and can improve blood flow to the brain, resulting in enhanced cognitive abilities.
4. Get Enough Sleep: Proper rest is vital for the brain to recharge and consolidate memories. Aim for 7-9 hours of sleep per night.
5. Manage Stress: Chronic Stress can negatively affect the brain, so practice relaxation techniques like breath focus, body scan and guided imagery.
6. SocialiseSocialise and Stay Connected: Participating in social activities and building and maintaining strong social connections can potentially lower the likelihood of cognitive decline.
Common Habits That Affect Brain Health
Some habits, if left unchecked, can harm our brain health. Here are a few to be mindful of:
1. Smoking: Smoking has the potential to harm blood vessels, leading to a decrease in blood circulation to the brain and an elevated risk of stroke and cognitive decline.
2. Excessive Alcohol Consumption: Heavy drinking can lead to brain shrinkage, memory problems, and cognitive impairment.
3. Poor Diet: A diet high in saturated fats, refined sugars, and processed foods may contribute to inflammation and oxidative Stress in the brain. Following the Mediterranean-DASH Diet Intervention for Neurodegenerative Delay, or MIND diet, tremendously affects overall health.
4. Lack of Physical Activity: A sedentary lifestyle can negatively impact brain health and increase the risk of cognitive decline. Exercise has incredible health benefits, and one thing it does is strengthen the heart muscles and make it better at pumping blood to other organs of the body, especially the brain.
5. Neglecting Mental Stimulation: Failing to engage in new activities and learn new things can cause your cognitive abilities to become stagnant. Loneliness is one factor that leads to mental decline among older adults. See how this digital health startup, Peppermint, is leveraging digital technology to combat loneliness among older people.
World Brain Day: Leave No One Behind

This year’s World Brain Health Day focuses on people with brain disabilities who don’t have equal access to brain healthcare.
According to the World Health Organisation (WHO), only about 25% of the world’s population has access to more than one trained neurologist per 100,000 people.
That’s a big gap. Not to mention the situation in developing countries, like in Africa or Asia, where it’s worse and the burden of lack of access to resources and trained personnel is felt more.
According to the World Federation of Neurology, these are the barriers to improving brain health:
- Poverty and Trauma
- Reallocation of Resources
- Scarcity of Public Health Resources
- Access to Specialists
- Cost of Treatment
These factors are complex and interrelated and can’t be solved at once. The most effective step we can take to mitigate the effect is to take advocacy seriously.
We must use our voices to advocate for people living with brain disability, make the government and stakeholders pay more attention to them, and start funding more researchers and allocating resources to brain healthcare.
We can also help spread accurate information about how people can take care of their brain health, detect brain disability early and quickly seek care, and provide information for those nursing brain disabilities on how to better take care of themselves.
Brain health includes various aspects such as cognitive, sensory, social-emotional, behavioural, and motor functioning.
Our pursuit of brain health for all must include all these vital dimensions.
This year’s World Brain Day aims to raise awareness about brain disability and let more people know how to detect, prevent and manage them.
On this World Brain Day, let’s take a moment to appreciate the incredible gift we have—our brains.
This is the right time to vow that you will take conscious and deliberate steps to care for your brain and position yourself to advocate for quality brain healthcare for all—leaving no one behind.
Research And Reports
Recommended Read On Care City
Epilepsy: Definition, Resources, Research & Reports
Here at Care City, we understand the power of information and how it can build people, families, organisations and nations.
We are dedicated to creating, curating and spreading the right information, and our focus is on leadership, innovation, entrepreneurship and creativity in healthcare.
If you spot anything that looks or sounds “out of the normal” or “extreme”, or “biased” kindly reach out to us, and we will immediately look into it [please use the contact box in the header or footer section].





