Mobile health applications, or mHealth apps, have emerged and earned their place as a powerful transforming tool in aiding healthcare delivery across the African continent.
The widespread use of smartphones and internet access in Africa has made it possible for mHealth apps to play a significant role in delivering healthcare services.
The International Communications Union reports that the percentage of individuals using the internet in the region grew from 9.6% in 2010 to 33% in 2021 (an impressive 23.4% increase in about ten years).
And the penetration of the internet on the continent keeps getting deeper, with internet providers like Starlink providing low-orbit internet access that can serve remote areas in Africa that do not have enough terrestrial and mobile internet infrastructure (deploying terrestrial and mobile internet infrastructure in these remote areas would incur high cost of installation, servicing and maintenance).
Two African countries, Nigeria and Mozambique, have already given Starlink regulatory approval to start operations.
These mobile applications have the potential to bridge gaps in healthcare delivery, provide accurate and safe medical information, and empower both healthcare professionals and users in Africa. However, their potential has yet to be fully realised.
In this post, we’ll explore the multifaceted role of mobile health applications in Africa, discussing their benefits, challenges with possible remedies, and their impact on the overall healthcare ecosystem in Africa.
Enhanced Healthcare Access And Delivery
Mobile health apps are a helpful solution to the challenges faced by people in Africa who have limited access to basic medical and healthcare services.
Digital health technologies, such as mobile health applications, can overcome obstacles people living in remote areas face, like distance, costly hospital visits, and the need for communication during isolation.
Mobile health applications incorporating advanced technologies, such as Natural Language Processing chatbots, have made it possible for telemedicine solutions to diagnose, treat, and prescribe medications (with guidance from a physician) for minor health issues remotely, eliminating the need for patients to travel long distances, spend money, or wait in hospital queues, making the process more convenient and comfortable.
Well-designed mobile health applications or telemedicine platforms that leverage artificial intelligence eliminate the need for unnecessary hospital visits, saving the time and money of both the patient and healthcare institutions.
The Covid-19 pandemic led to a rapid increase in the use of healthcare applications or digital health technologies.
Due to the pandemic, isolation protocols limited healthcare access, which prevented people from going to hospitals. As a result, people relied on mobile healthcare applications for their basic healthcare needs. For those who needed to go to the hospital, doctors conducted virtual consultations advising patients to come to the hospital if necessary.
Mobihealth is an example of a telemedicine platform in Nigeria that provides affordable healthcare services via their mobile application to people in Nigeria who may not have immediate access to certain basic medical services or those who don’t just want to go through the stress of travelling to the hospital to see a doctor.
Mobihealth offers remote diagnostics services through its POCUS modules, telehealth services, integrated telehealth clinics, home health, and EMR services.
Health Education And Awareness
There already exists a paucity of accurate healthcare information on the internet. It’s sometimes difficult to tell what’s scientifically proven right in a heavily overloaded online world of healthcare information.
And most people admit to getting most of their healthcare information online.
It’ll even interest you to know that 5% of all Google searches are health-related.
Inaccurate and unverified healthcare information from unregulated online sources could expose people who don’t have enough knowledge of healthcare to significant harm and risk.
Mobile healthcare applications can mitigate this gap by ensuring the quality of healthcare information featured on their platform is scientifically accurate and updated.
Innovative healthcare applications can meet the information needs of certain groups of people who suffer from diseases like diabetes, obesity, or cancer, as well as vulnerable groups like pregnant mothers, people with disabilities, and the elderly. These apps can help reduce the disease burden on patients, families, and healthcare institutions by providing individuals with the right information to care for themselves and seek prompt intervention if they detect any abnormalities in their health.
In Africa, a couple of mobile health applications offer consumers verified and scientifically accurate healthcare information. Like the Omomi app, which provides information about growth patterns and general health information about babies, general infant health tips, and the Smart Health App, which provides accurate information about disease conditions like HIV/AIDS, TB, and Malaria.
Mobile Monitoring And Diagnostics
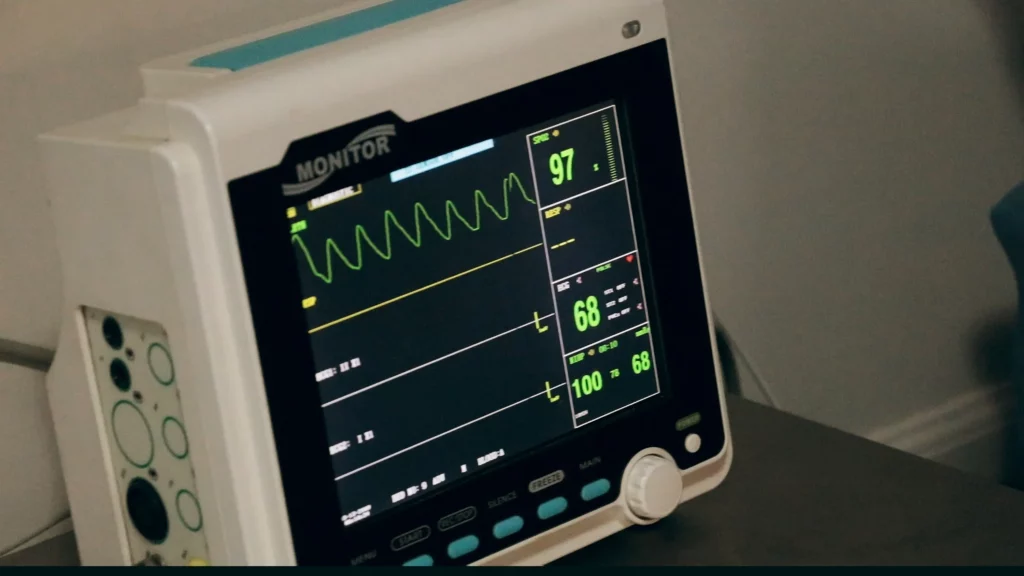
Remote patient health status tracking is quite a groundbreaking technology.
Wearables can monitor heart rate, ECG, saturation and other basic physiological parameters.
Most wearables are integrated with mobile health applications, with some more advanced ones connected to cloud services where healthcare professionals can monitor patients and clients remotely.
Global technology brands like Oraimo dominate the African wearable market with smartwatches and fitness trackers that monitor a wide range of basic physiological parameters like heart rate, ECGs, respiratory rate and blood pressure.
Wearable and fitness gadgets and technology play an important role in managing conditions like heart failure, diabetes, and mental disorders.
These devices can quickly and conveniently gather real-time physiological data that healthcare professionals or AI constantly monitor. This allows abnormalities to be detected promptly, ensuring timely intervention before irreversible damage occurs.
Strengthening Healthcare Systems
In Africa, public healthcare systems are already under a heavy burden to cater to the healthcare needs of overpopulated communities.
With the current massive movement of healthcare professionals out of the continent in search of greener pastures, resulting in unprecedented brain drain coupled with other factors like poor leadership and lack of basic social amenities, public healthcare institutions on the continent are already under stress.
Digital health technologies, like mobile health applications, play strategic roles in strengthening African healthcare systems by taking some of the burden away from traditional hospitals or clinics.
There are basic services that these mobile health applications and platforms can easily and conveniently provide to patients and clients without them bothering themselves going to a physical hospital.
In Africa, public healthcare systems spend more resources (that they are trying to manage) attending to patients in person, even though some of their needs could be addressed more efficiently through mobile health platforms. This could help alleviate the burden on hospitals and improve access to healthcare services for patients, while in turn strengthening already weak healthcare systems.
In addition, utilizing mobile health platforms has proven to be an effective means of streamlining the upkeep of administrative and operational processes within healthcare systems.
This technology offers extensive benefits, particularly in the areas of data and inventory management.
By leveraging mobile health platforms, healthcare systems can efficiently manage crucial administrative tasks while improving the overall quality of patient care.
With these tools at their disposal, healthcare institutions in Africa can focus on delivering top-notch healthcare services while leaving the cumbersome administrative tasks to digital health technologies like mobile healthcare applications or platforms.
Challenges And Future Directions

It has been reported that over a billion individuals worldwide have utilised health-promoting mobile apps. However, there still needs to be enough research and evidence to validate their clinical effectiveness.
Integrating these apps with clinical electronic health records could go a long way in improving coordinated healthcare.
However, the digital divide poses a challenge as people without internet access are left out.
Access to personal health records through computers has been lower among disadvantaged populations, but the widespread availability of smartphones has increased mobile access.
Mobile-accessible personal health records can help patients manage their health, especially for conditions like diabetes that need close monitoring and prompt intervention in the case of an emergency.
Mobile access has bridged the gap and facilitated the use of personal health records among those who rely on their mobile devices, leading to improved healthcare outcomes.
In the healthcare industry, robust data protection measures and regulations are essential for safeguarding patient personal information.
Addressing cybersecurity threats and potential data breaches becomes crucial as reliance on digital health records increases.
Implementing data encryption, data masking, disaster recovery planning, and tokenisation measures will significantly enhance data security and manage patient data.
Additionally, ensuring user privacy, implementing security policies, and employing technological solutions are integral components of a comprehensive data security framework. And above all, creating systems that make the interoperability of digital health data possible or easy.
Mobile Health Applications are just one of many technological advancements improving our world.
And as we progress in the dynamic world of digital health technologies, whole societies must adjust to the reality and allow these technologies to melt into the already existing fabric of society seamlessly.

Our editorial team writes and curates a newsletter on Substack, Care City Weekly.
You’ll find it interesting if you love healthcare leadership, innovation, creativity and entrepreneurship. We publish it once or twice a month (or more) and it’s free. Check it out here.
Our Substack newsletter brings together our favourite articles of the week (or month) and also features articles, stories and reports from leading healthcare publications and mainstream publications (and from some alternative media sources).
You can also check The Digital Health Report, our publication dedicated to stories and reports about digital health.






Drop Your Comment